The readline module defines a number of functions to facilitatecompletion and reading/writing of history files from the Python interpreter.This module can be used directly, or via the rlcompleter module, whichsupports completion of Python identifiers at the interactive prompt. Settingsmade using this module affect the behaviour of both the interpreter'sinteractive prompt and the prompts offered by the built-in input()function.
- Pyserial Readline Example
- Readline In Python
- Python File Readlines
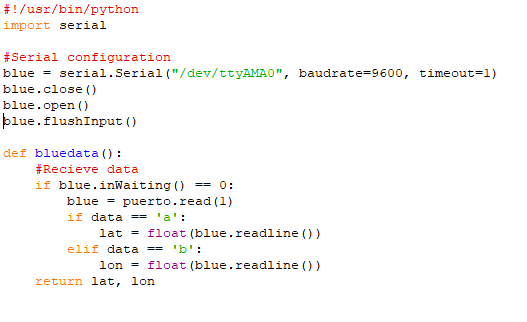
- Python Pyserial Read Example
- Pyserial Example Code
- Python Pyserial Readline Example Python
Readline keybindings may be configured via an initialization file, typically.inputrc in your home directory. See Readline Init Filein the GNU Readline manual for information about the format andallowable constructs of that file, and the capabilities of theReadline library in general.
Note
The underlying Readline library API may be implemented bythe libedit library instead of GNU readline.On macOS the readline module detects which library is being usedat run time.
The configuration file for libedit is different from thatof GNU readline. If you programmatically load configuration stringsyou can check for the text 'libedit' in readline.__doc__to differentiate between GNU readline and libedit.
If you use editline/libedit readline emulation on macOS, theinitialization file located in your home directory is named.editrc. For example, the following content in ~/.editrc willturn ON vi keybindings and TAB completion:
Init file¶
Python Serial - 30 examples found. These are the top rated real world Python examples of serial.Serial extracted from open source projects. You can rate examples to help us improve the quality of examples. Python Datalogger - Using pySerial to Read Serial Data Output from Arduino After I became proficient with Arduino I found myself trapped in its development environment (IDE). I needed to escape from the simplicity of the serial port and transform the platform into a usable engineering tool. Python Serial.readuntil - 4 examples found. These are the top rated real world Python examples of serial.Serial.readuntil extracted from open source projects. You can rate examples to help us improve the quality of examples. Do also have a look at the example files in the examples directory in the source distribution or online. Note The eol parameter for readline is no longer supported when pySerial is run with newer Python versions (V2.6+) where the module io is available. Interface Python and Arduino With PySerial: Over the last few months I have learned how to program with Python. With one of the upcoming projects that I am working on it would be nice to have a computer's display to view the data collected by a rover in real-time as well as crunch numbers whi.
The following functions relate to the init file and user configuration:
readline.parse_and_bind(string)¶Execute the init line provided in the string argument. This callsrl_parse_and_bind() in the underlying library.
readline.read_init_file([filename])¶Execute a readline initialization file. The default filename is the last filenameused. This calls rl_read_init_file() in the underlying library.
Line buffer¶
The following functions operate on the line buffer:
readline.get_line_buffer()¶Return the current contents of the line buffer (rl_line_bufferin the underlying library).
readline.insert_text(string)¶Insert text into the line buffer at the cursor position. This callsrl_insert_text() in the underlying library, but ignoresthe return value.
readline.redisplay()¶Change what's displayed on the screen to reflect the current contents of theline buffer. This calls rl_redisplay() in the underlying library.
History file¶
The following functions operate on a history file:
readline.read_history_file([filename])¶Load a readline history file, and append it to the history list.The default filename is ~/.history. This callsread_history() in the underlying library.
readline.write_history_file([filename])¶Pyserial Readline Example

Save the history list to a readline history file, overwriting anyexisting file. The default filename is ~/.history. This callswrite_history() in the underlying library.
readline.append_history_file(nelements[, filename])¶Append the last nelements items of history to a file. The default filename is~/.history. The file must already exist. This callsappend_history() in the underlying library. This functiononly exists if Python was compiled for a version of the librarythat supports it.
readline.get_history_length()¶readline.set_history_length(length)¶Set or return the desired number of lines to save in the history file.The write_history_file() function uses this value to truncatethe history file, by calling history_truncate_file() inthe underlying library. Negative values implyunlimited history file size.
History list¶
The following functions operate on a global history list:
readline.clear_history()¶Readline In Python
Clear the current history. This calls clear_history() in theunderlying library. The Python function only exists if Python wascompiled for a version of the library that supports it.
readline.get_current_history_length()¶Return the number of items currently in the history. (This is different fromget_history_length(), which returns the maximum number of lines that willbe written to a history file.)
readline.get_history_item(index)¶Return the current contents of history item at index. The item indexis one-based. This calls history_get() in the underlying library.
readline.remove_history_item(pos)¶Remove history item specified by its position from the history.The position is zero-based. This calls remove_history() inthe underlying library.
readline.replace_history_item(pos, line)¶Replace history item specified by its position with line.The position is zero-based. This calls replace_history_entry()in the underlying library.
readline.add_history(line)¶Append line to the history buffer, as if it was the last line typed.This calls add_history() in the underlying library.
readline.set_auto_history(enabled)¶Enable or disable automatic calls to add_history() when readinginput via readline. The enabled argument should be a Boolean valuethat when true, enables auto history, and that when false, disablesauto history.
CPython implementation detail: Auto history is enabled by default, and changes to this do not persistacross multiple sessions.
Startup hooks¶
readline.set_startup_hook([function])¶Set or remove the function invoked by the rl_startup_hookcallback of the underlying library. If function is specified, it willbe used as the new hook function; if omitted or None, any functionalready installed is removed. The hook is called with noarguments just before readline prints the first prompt.
readline.set_pre_input_hook([function])¶Set or remove the function invoked by the rl_pre_input_hookcallback of the underlying library. If function is specified, it willbe used as the new hook function; if omitted or None, anyfunction already installed is removed. The hook is calledwith no arguments after the first prompt has been printed and just beforereadline starts reading input characters. This function only existsif Python was compiled for a version of the library that supports it.
Completion¶
The following functions relate to implementing a custom word completionfunction. This is typically operated by the Tab key, and can suggest andautomatically complete a word being typed. By default, Readline is set upto be used by rlcompleter to complete Python identifiers forthe interactive interpreter. If the readline module is to be usedwith a custom completer, a different set of word delimiters should be set.
readline.set_completer([function])¶Set or remove the completer function. If function is specified, it will beused as the new completer function; if omitted or None, any completerfunction already installed is removed. The completer function is called asfunction(text,state), for state in 0, 1, 2, …, until itreturns a non-string value. It should return the next possible completionstarting with text.
The installed completer function is invoked by the entry_func callbackpassed to rl_completion_matches() in the underlying library.The text string comes from the first parameter to therl_attempted_completion_function callback of theunderlying library.
readline.get_completer()¶Python File Readlines
Get the completer function, or None if no completer function has been set.
Python Pyserial Read Example
readline.get_completion_type()¶Get the type of completion being attempted. This returns therl_completion_type variable in the underlying library asan integer.
readline.get_begidx()¶
readline.get_line_buffer()¶Return the current contents of the line buffer (rl_line_bufferin the underlying library).
readline.insert_text(string)¶Insert text into the line buffer at the cursor position. This callsrl_insert_text() in the underlying library, but ignoresthe return value.
readline.redisplay()¶Change what's displayed on the screen to reflect the current contents of theline buffer. This calls rl_redisplay() in the underlying library.
History file¶
The following functions operate on a history file:
readline.read_history_file([filename])¶Load a readline history file, and append it to the history list.The default filename is ~/.history. This callsread_history() in the underlying library.
readline.write_history_file([filename])¶Pyserial Readline Example
Save the history list to a readline history file, overwriting anyexisting file. The default filename is ~/.history. This callswrite_history() in the underlying library.
readline.append_history_file(nelements[, filename])¶Append the last nelements items of history to a file. The default filename is~/.history. The file must already exist. This callsappend_history() in the underlying library. This functiononly exists if Python was compiled for a version of the librarythat supports it.
readline.get_history_length()¶readline.set_history_length(length)¶Set or return the desired number of lines to save in the history file.The write_history_file() function uses this value to truncatethe history file, by calling history_truncate_file() inthe underlying library. Negative values implyunlimited history file size.
History list¶
The following functions operate on a global history list:
readline.clear_history()¶Readline In Python
Clear the current history. This calls clear_history() in theunderlying library. The Python function only exists if Python wascompiled for a version of the library that supports it.
readline.get_current_history_length()¶Return the number of items currently in the history. (This is different fromget_history_length(), which returns the maximum number of lines that willbe written to a history file.)
readline.get_history_item(index)¶Return the current contents of history item at index. The item indexis one-based. This calls history_get() in the underlying library.
readline.remove_history_item(pos)¶Remove history item specified by its position from the history.The position is zero-based. This calls remove_history() inthe underlying library.
readline.replace_history_item(pos, line)¶Replace history item specified by its position with line.The position is zero-based. This calls replace_history_entry()in the underlying library.
readline.add_history(line)¶Append line to the history buffer, as if it was the last line typed.This calls add_history() in the underlying library.
readline.set_auto_history(enabled)¶Enable or disable automatic calls to add_history() when readinginput via readline. The enabled argument should be a Boolean valuethat when true, enables auto history, and that when false, disablesauto history.
CPython implementation detail: Auto history is enabled by default, and changes to this do not persistacross multiple sessions.
Startup hooks¶
readline.set_startup_hook([function])¶Set or remove the function invoked by the rl_startup_hookcallback of the underlying library. If function is specified, it willbe used as the new hook function; if omitted or None, any functionalready installed is removed. The hook is called with noarguments just before readline prints the first prompt.
readline.set_pre_input_hook([function])¶Set or remove the function invoked by the rl_pre_input_hookcallback of the underlying library. If function is specified, it willbe used as the new hook function; if omitted or None, anyfunction already installed is removed. The hook is calledwith no arguments after the first prompt has been printed and just beforereadline starts reading input characters. This function only existsif Python was compiled for a version of the library that supports it.
Completion¶
The following functions relate to implementing a custom word completionfunction. This is typically operated by the Tab key, and can suggest andautomatically complete a word being typed. By default, Readline is set upto be used by rlcompleter to complete Python identifiers forthe interactive interpreter. If the readline module is to be usedwith a custom completer, a different set of word delimiters should be set.
readline.set_completer([function])¶Set or remove the completer function. If function is specified, it will beused as the new completer function; if omitted or None, any completerfunction already installed is removed. The completer function is called asfunction(text,state), for state in 0, 1, 2, …, until itreturns a non-string value. It should return the next possible completionstarting with text.
The installed completer function is invoked by the entry_func callbackpassed to rl_completion_matches() in the underlying library.The text string comes from the first parameter to therl_attempted_completion_function callback of theunderlying library.
readline.get_completer()¶Python File Readlines
Get the completer function, or None if no completer function has been set.
Python Pyserial Read Example
readline.get_completion_type()¶Get the type of completion being attempted. This returns therl_completion_type variable in the underlying library asan integer.
readline.get_begidx()¶readline.get_endidx()¶Get the beginning or ending index of the completion scope.These indexes are the start and end arguments passed to therl_attempted_completion_function callback of theunderlying library.
readline.set_completer_delims(string)¶readline.get_completer_delims()¶Set or get the word delimiters for completion. These determine thestart of the word to be considered for completion (the completion scope).These functions access the rl_completer_word_break_charactersvariable in the underlying library.
readline.set_completion_display_matches_hook([function])¶Pyserial Example Code
Set or remove the completion display function. If function isspecified, it will be used as the new completion display function;if omitted or None, any completion display function alreadyinstalled is removed. This sets or clears therl_completion_display_matches_hook callback in theunderlying library. The completion display function is called asfunction(substitution,[matches],longest_match_length) onceeach time matches need to be displayed.
Example¶
The following example demonstrates how to use the readline module'shistory reading and writing functions to automatically load and save a historyfile named .python_history from the user's home directory. The codebelow would normally be executed automatically during interactive sessionsfrom the user's PYTHONSTARTUP file.
This code is actually automatically run when Python is run ininteractive mode (see Readline configuration).
The following example achieves the same goal but supports concurrent interactivesessions, by only appending the new history.
Python Pyserial Readline Example Python
The following example extends the code.InteractiveConsole class tosupport history save/restore.

